- Year 2018
- Theme Health - Maternal and Child Health
- Team Behavioural Insights Unit of India, NITI Aayog
Partnerships
- Aspirational Districts Programme, NITI Aayog
- The Curve


Please find below the key documents
In 2018-19, CSBC developed and tested behavioural interventions to increase adherence to Iron and Folic Acid (IFA) tablet consumption by pregnant women.
In collaboration with the Aspirational Districts Programme (ADP) and The Curve the NITI-BIU developed comprehensive guidelines to facilitate the scale-up of the IFA interventions across India.
Over the years, there has been an increase in the prevalence of anaemia in women. As of 2019-20, 57% of women in the reproductive age group (15-49 years) are anaemic as compared to 53.1% in 2015-16. Similarly, 52.2% of pregnant women in India are anaemic in 2019-20 as compared to 50.4% in 2015-16.
A major barrier to the reduction in the incidence of anaemia among pregnant women is the low uptake of and adherence to the IFA tablets. As of 2019-20, only 26% of pregnant women consumed the recommended dosage of IFA tablets for 180 days.
The condition is associated with significant adverse maternal and child health outcomes. Intrauterine deaths are 3.7 times more likely among anaemic women, prematurity is four times more likely, and low birth weight is 1.9 times more likely among infants born to anaemic mothers as compared to mothers who are not anaemic. Twenty per cent of all maternal deaths can be directly attributed to anaemia and another 50% are indirectly related to it.
To lower the incidence of anaemia among pregnant women, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) has been disbursing IFA tablets to pregnant women under various health programmes. It is recommended that pregnant women in their 2nd and 3rd trimesters consume these pills everyday (around 180 days). As a part of the same, pregnant women are provided with IFA tablets through ANMs at various platforms including the Village Health Sanitation and Nutrition Day (VHSND) and the Ante Natal Care check-up on the 9th of every month under the Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyaan (PMSMA). Currently, all anaemia-related activities are conducted under the Anaemia Mukt Bharat (AMB) Strategy.
In 2018, CSBC in partnership with Research Triangle Institute (RTI) International, conducted a diagnostic study to identify behavioural barriers to the uptake of and adherence to IFA tablets. The identified behavioural barriers are:
Based on the barriers, five interventions were designed and tested in a lab - in the - field experiment in Haryana (2018) and a Randomised Control Trial (RCT) in Madhya Pradesh (2019).Two interventions that proved to be effective in increasing the consumption of IFA tablets were the counselling card and the goal tracking calendar.
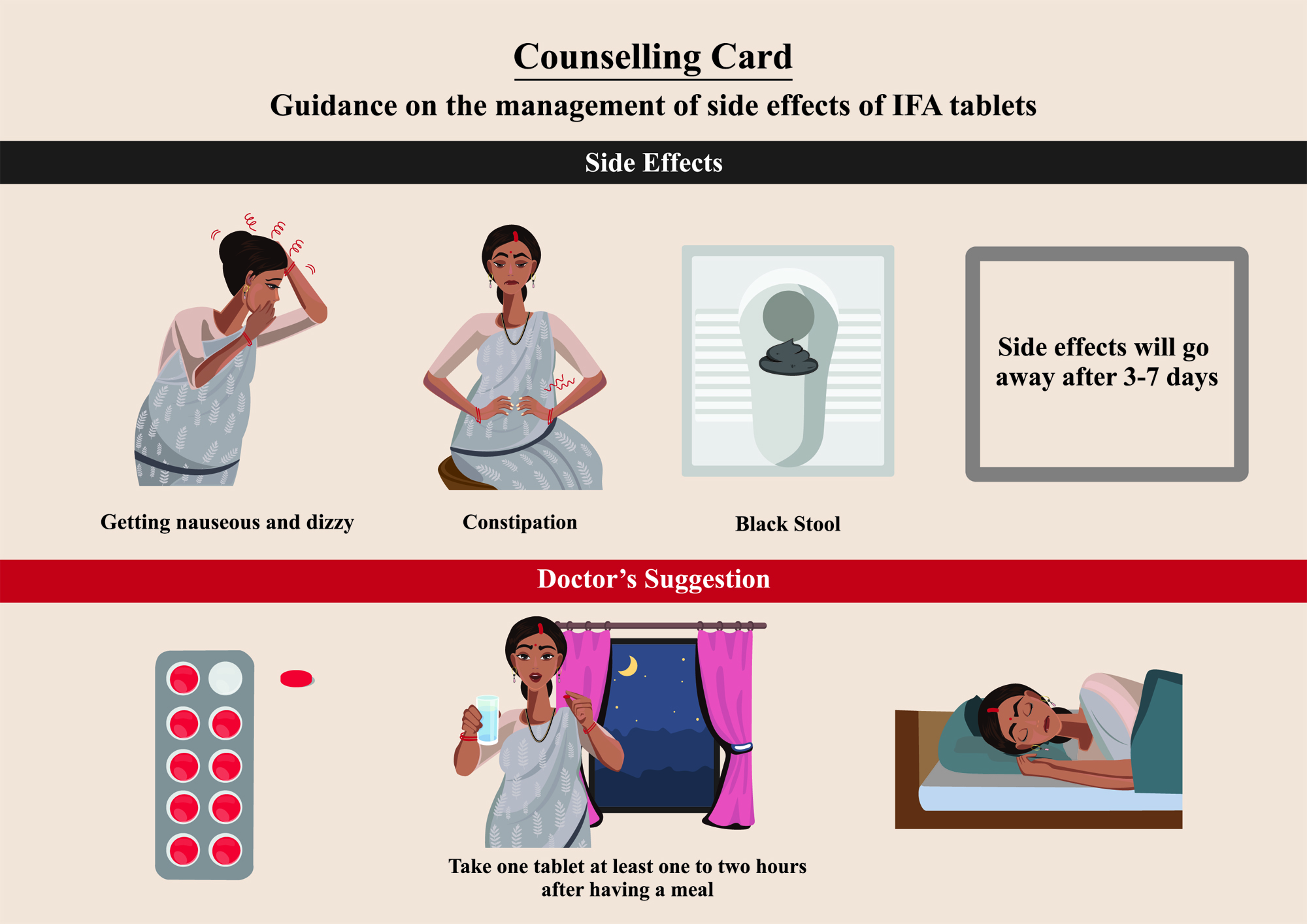
Lack of adherence to the consumption of IFA tablets due to their side effects
The card makes information on the side effects of IFA tablets and the management of side effects salient
Frontline Health Workers may use the card to counsel pregnant women at the time of distribution of IFA tablets

Deprioritization of the consumption of IFA tablets as their benefits are not salient
The calendar makes the benefits of the IFA tablets salient by demonstrating visual progress and helping in the recall of their consumption
Pregnant women may scratch off a cell on the calendar every time they consume an IFA tablet
In 2022, NITI-BIU in partnership with The Curve conducted a qualitative to understand how to best integrate the counselling card and goal-tracking calendar within the existing health machinery of India without disturbing pre-existing dynamics. A three-step approach was adopted for the same. The approach involved conducting the following:
The findings from the study lead to the creation of operational guidelines for the two interventions. The guidelines lay down the key features of the behavioural interventions and the operational steps involved in their implementation. They provide a framework for effective scale-up of the counselling card and the goal tracking calendar and facilitate their implementation through different stages of programme delivery.
Behavioural Insights Unit of India, NITI Aayog